User Tools
Table of Contents
SPF, DKIM and DMARC
 Incomplete
Incomplete
SPF (sender policy framework), DKIM (domain keys identified mail) and DMARC (domain message authentication reporting and conformance) are sender authentication mechanisms that use DNS.
Testing
Various Tools: https://dmarcian.com/dmarc-tools/
DKIM Test Tool: https://mxtoolbox.com/dkim.aspx
DMARC Test Tool: https://mxtoolbox.com/DMARC.aspx
A very useful test is to send a message from the domain under test to a Gmail address. Once the message is received in Gmail, perform a Show Original to view the message headers.
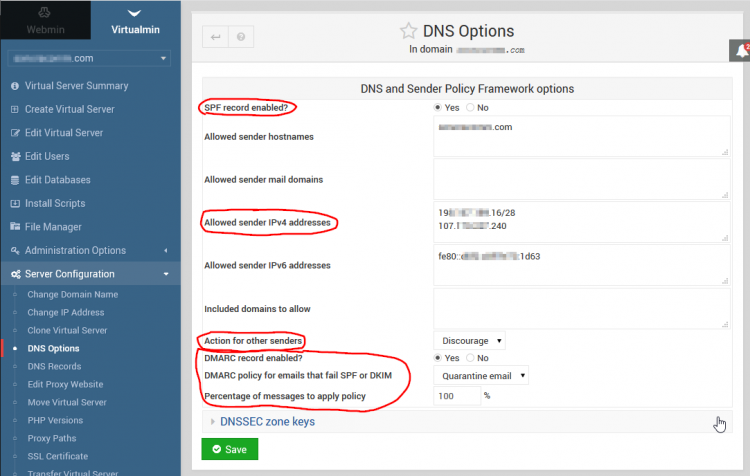
SPF
SPF is the most widely used sender authentication mechanism. You should definitely implement it for your domains.
A DNS SPF (TXT) record just tells the recipient server which sender servers are authorized to send e-mail for a particular domain.
Virtualmin
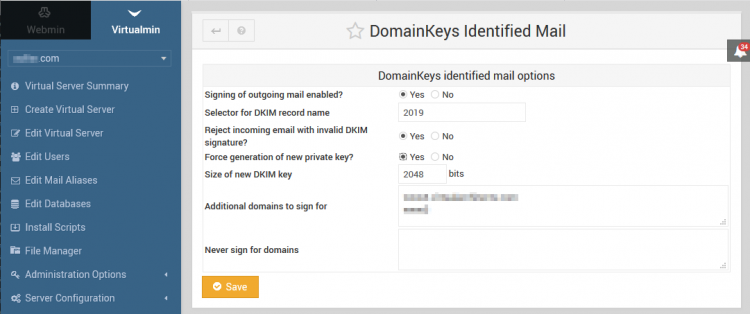
DKIM
DKIM is a standard for signing email messages so that the recipient can verify the sender's email address. This allows recipient mail servers to detect sender address forgery, which is often used by spammers to avoid sender domain blacklists.
Signing is done with a private key on the sender's server, which matches a public key added to in the sender's DNS domain. The recipient can lookup this key at the domain in the From address, and use it to ensure that the email signature was created using the corresponding private key, which proves that the message was really sent from that domain.
Virtualmin
https://www.virtualmin.com/documentation/email/dkim
Virtualmin uses a milter (daemon) to implement DKIM signing and verification.
Virtualmin → E-Mail Settings → DomainKeys Identified Mail
Zimbra
Important: https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Configuring_for_DKIM_Signing
https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Best_Practices_on_Email_Protection:_SPF,_DKIM_and_DMARC
DMARC
DMARC is a mechanism to tell receiving mail servers exactly how to treat failures of SPF and DKIM checks.
DMARC also includes a mechanism to report failures back to administrators of sender domains.