User Tools
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Syslog with Graylog
 Unfinished
Unfinished
Excellent Documentation: https://docs.graylog.org/en/4.1/index.html
Installation: https://docs.graylog.org/en/4.1/pages/installation/os/ubuntu.html#ubuntuguide
Install Graylog OSS on Ubuntu: https://www.itzgeek.com/how-tos/linux/ubuntu-how-tos/how-to-install-graylog-on-ubuntu-20-04.html
Getting Started: http://123.123.123.123:9000/gettingstarted
Getting Started Docs: https://docs.graylog.org/en/4.1/pages/getting_started.html
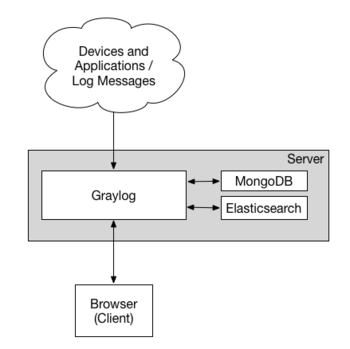
Graylog is a web interface to your syslog server, and much more. It is available in a free open source edition as well as commercial editions with more features.
To scale well, Graylog depends on:
- Fast CPUs (Graylog)
- Lots of RAM (Elasticsearch)
- Fast storage (Elasticsearch)
Active, searchable data is in memory and easily lost.
Archived data is stored in a compressed format on the Graylog server or network file share. It is searchable via GREP, but must be reconstituted in Graylog in order to be searchable through the GUI again.
Configuration
The Graylog configuration file is /etc/graylog/server/server.conf.
The Elasticsearch config file is: /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.
Syslog Input
The first step to accept input is to create an Input, probably syslog UDP and TCP.
To accept input data on ports below 1024, we must either run Graylog as root or use redirection to a higher port.
It is recommended to configure the syslog Input to accept traffic on UDP port 1514 and redirect traffic sent to UDP 514 to it.
See also https://virtualarchitects.com/wiki/doku.php?id=networking:firewall:csf
Older Syslog Info
Assumptions:
- Your local network is 192.168.1.0/24
- The host you'd like to log for is also on that network
- You are only using IPv4
CentOS 5 Server
Firewall
Open the server's firewall to listen on UDP port 514:
vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Insert:
-A INPUT –s 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0 -m udp -p udp --dport 514 -j ACCEPT
Save, exit and restart iptables:
service iptables restart
Configure Syslog
vim /etc/sysconfig/syslog
Modify the existing line by adding -r:
SYSLOGD_OPTIONS="-m 0 -r"
Then restart syslog:
service syslog restart
Verify that syslog is monitoring port 514:
netstat –anp | grep 514
If you get no result, then something's wrong. If you get a result, then syslog is working and monitoring port 514.
Configure syslog to create a logfile for your device:
vim /etc/syslog.conf
Add these lines:
# Describe host you're logging here *.* /etc/log/yourlogfilename.log
Note: the spaces between . and /etc/log/… must be inserted using the TAB key! logfilename.log can be whatever name you want for your logfile.
Set-up whatever device allows for syslog and give it the IP address of your PBX system. If you want another CentOS machine to send logs to yours, then
vim /etc/syslog.conf
Add a line like this:
*.* @IPADDRESSOFRECEIVING MACHINE
Note: the spaces between . and @IPADDRESS must be inserted using the TAB key!
To view the logfile:
tail -f /var/log/yourlogfilename.log