User Tools
Table of Contents
Syslog with Graylog
Excellent Documentation: https://docs.graylog.org/en/4.1/index.html
Installation: https://docs.graylog.org/en/4.1/pages/installation/os/ubuntu.html#ubuntuguide
Install Graylog OSS on Ubuntu: https://www.itzgeek.com/how-tos/linux/ubuntu-how-tos/how-to-install-graylog-on-ubuntu-20-04.html
Getting Started: https://docs.stackhero.io/en/Graylog
Getting Started Docs: https://docs.graylog.org/en/4.1/pages/getting_started.html
https://docs.graylog.org/en/3.1/pages/faq.html#how-can-i-start-an-input-on-a-port-below-1024
https://github.com/Graylog2/graylog-guide-syslog-linux
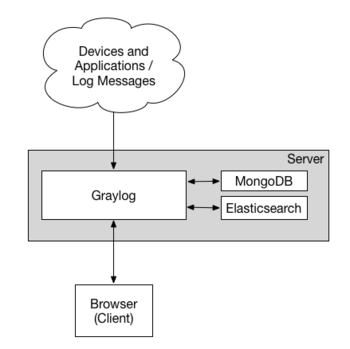
Graylog is a web interface to your syslog server, and much more. It is available in a free open source edition as well as commercial editions with more features.
To scale well, Graylog depends on:
- Fast CPUs (Graylog)
- Lots of RAM (Elasticsearch)
- Fast storage (Elasticsearch)
Active, searchable data is in memory and easily lost.
Archived data is stored in a compressed format on the Graylog server or network file share. It is searchable via GREP, but must be reconstituted in Graylog in order to be searchable through the GUI again.
Upgrade
We use apt repositories for installation, so updates are easy:
Show all apt sources:
grep -r --include '*.list' '^deb ' /etc/apt/sources.list*
apt update && apt dist-upgrade -y && apt autoremove -y && apt clean && reboot
Configuration
The Graylog configuration file is /etc/graylog/server/server.conf.
The Elasticsearch config file is: /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.
Syslog Input
The first step to accept input is to create an Input (listener), perhaps “Syslog UDP”.
It is recommended to configure the syslog Input to accept traffic on UDP port 1514 and redirect traffic sent to UDP 514 to it.
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 514 -j REDIRECT --to 1514 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p udp --dport 514 -j REDIRECT --to 1514
See also https://virtualarchitects.com/wiki/doku.php?id=networking:firewall:csf
Create Index
Indexes are how data is stored and rotated.
Create Stream
Stream Rules route or sort messages into indexes.