Table of Contents
Proxmox Virtualization Environment

Main: https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-ve
Wiki: http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/
Documentation: https://pve.proxmox.com/pve-docs/
Forums: http://forum.proxmox.com/
Proxmox VE is a 64-bit, free, open-source, bare-metal virtualization platform (hypervisor).
Proxmox VE provides two virtualization technologies in one platform:
- OpenVZ Containers
- Linux KVM
KVM requires hardware (CPU+mainboard) virtualization support.
Administration
Proxmox VE Clusters can be managed from any of the cluster hosts.
https://<ipaddress>:8006
Installation
![]() Use Etcher to write the ISO to a flash drive.
Use Etcher to write the ISO to a flash drive.
![]() The installer is graphical and requires a mouse.
The installer is graphical and requires a mouse.
Download: https://www.proxmox.com/en/downloads
Updating and Upgrading
![]() Proxmox VE comes pre-configured to use the 'enterprise' (paid subscription) package repository.
Proxmox VE comes pre-configured to use the 'enterprise' (paid subscription) package repository.
No Subscription
If you don't have a subscription, you must reconfigure the repository:
First, comment out the 'enterprise' repo:
vi /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-enterprise.list
Then clone the 'enterprise' repo file and modify it:
cp -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-enterprise.list /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-no-sub.list vi /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pve-no-sub.list deb http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pve buster pve-no-subscription apt update apt dist-upgrade reboot
Windows Guests
Windows 7: https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Windows_7_guest_best_practices
Windows 8: https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Windows_8_guest_best_practices
Windows 10: https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Windows_10_guest_best_practices
Windows 2012: https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Windows_2012_guest_best_practices
 All very old below this point!
All very old below this point!
PVE Host Networking
If you set a static IP address for the PVE host using the web interface post-installation, you may find the wrong IP address shown at the SSH login prompt. Edit /etc/hosts to fix:
nano /etc/hosts reboot
Quickie Performance Test
On the Hardware Node (HN):
pveperf
Proxmox VE 2.x With Software RAID
KVM
http://c-nergy.be/blog/?p=1004
http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page
KVM provides for full virtualization and is built into the Linux kernel. It's supported by Redhat, Ubuntu and other distributions.
Live Migration
![]() Live migration with KVM requires that you store your VM data on NAS/SAN or DRBD.
Live migration with KVM requires that you store your VM data on NAS/SAN or DRBD.
Disk Image Format
- Raw
- Better performance than qcow2
- The full size will be provisioned on the proxmox host server (thick provisioning)
- QCOW
- Supports snapshots
- The full size will not be provisioned at first (thin provisioning)
- Can use copy on write technology
- VMDK
- Supports thin provisioning
- More compatible with VMware
VirtIO
- KVM guest drivers are built into many Linux distributions.
- KVM Windows guest drivers are updated frequently and readily available:
OpenVZ
http://wiki.openvz.org/Main_Page
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/OpenVZ_Console
OpenVZ Containers work differently than KVM, VMware or Xen technologies:
- Uses the same Linux kernel that's running on the host machine
- Probably provides the fastest virtualization
- Has near-zero overhead
- Only works for Linux guests
CentOS 5 Container (VM)
When you first create a CentOS 5 VM, you must reconfigure a few things: From the PVE host CLI, we enter the VM:
vzctl enter CTID #next steps are all now inside the VM
Enable Proxmox CT console so we can access it from the web management interface:
vim /etc/inittab
Add the following line and reboot:
1:2345:respawn:/sbin/agetty tty1 38400 linux
CentOS 6 Container (VM)
When you first create a CentOS 6 VM, you must reconfigure a few things: From the PVE host CLI, we enter the VM:
vzctl enter CTID #next steps are all now inside the VM
Enable Proxmox CT console so we can access it from the web management interface:
vim /etc/init/tty.conf # This service maintains a getty on tty1 from the point the system is # started until it is shut down again. start on stopped rc RUNLEVEL=[2345] stop on runlevel [!2345] respawn exec /sbin/agetty -8 tty1 38400
Then reboot the VM.
Networking
Differences Between venet and veth: http://wiki.openvz.org/Differences_between_venet_and_veth
Detailed veth Networking Info: http://forum.openvz.org/index.php?t=msg&&th=6191&goto=36869#msg_36869
venet Docs: http://openvz.org/Virtual_network_device
veth Docs: http://openvz.org/Virtual_Ethernet_device
- Proxmox VE uses a bridged networking model
- All VMs can share one bridge as if virtual network cables from each guest were all plugged into the same switch
- For connecting VMs to the outside world, bridges are attached to physical network cards and assigned a TCP/IP configuration
- VLANs (IEEE 802.1q) and network bonding/aggregation are possible with KVM
venet
- Networking configuration is assigned by OpenVZ admin
- Possibly more secure since VM owners can't set the IP addresses
- Possibly faster than
veth
veth
- More like regular Linux networking
- Networking configuration is assigned by VM owner
- Has MAC address to support more networking configurations
- Used to get an IP address from your DHCP server
- Works with a pair of interfaces connected together
- One in the host OS (host node, container zero, HN, CT0) and the other in the CT (container)
- Packets sent to the HN interface come out in the CT
Multiple NICs for OpenVZ Containers
venet
- You can assign multiple IP addresses
- Just add them after you created the container (separated with spaces) using the GUI
veth
- Use the CLI
- See 'man vzctl'
Java VNC Console
If you have problems using the VNC Console links, verify that you have Sun/Oracle Java installed.
It seems to work fine with Java 6 or Java 7.
See also Fedora 16 Notes.
Backup
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Backup_and_Restore
If you want to back up to and additional hard drive in your Proxmox server, you'll want to prep it and mount it manually. Then you can configure the backup in the web interface.
Prep the Disk
Create one large partition on the extra disk and create a filesystem. After that, create a mount point and create an entry in /etc/fstab. Finally, configure the directory /backup in the storage-gui.
fdisk -l fdisk /dev/sdd mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdd1 mkdir /mnt/backup blkid
Edit /etc/fstab and add:
vim /etc/fstab # Mount sdd1 as backup storage using the UUID UUID=549b77bf-be9a-4bed-b56f-ab360004717c /mnt/backup ext3 defaults,noatime 0 0
mount -a mount /dev/sdd1 on /mnt/backup type ext3 (rw,noatime)
Configure the Storage
Configuration → Storage → Add Directory
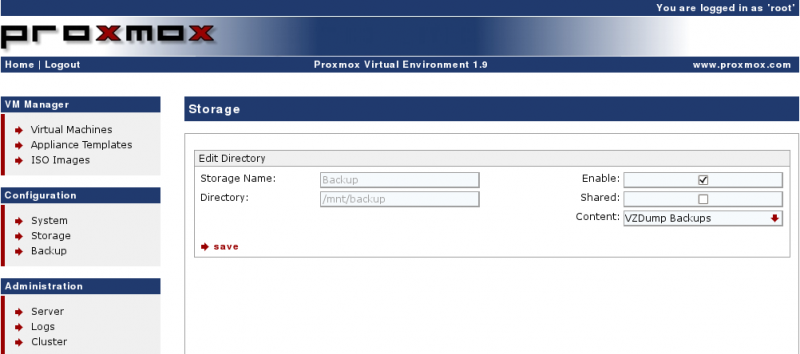
Configure the Backup Job
Configuration → Backup → Create New Job
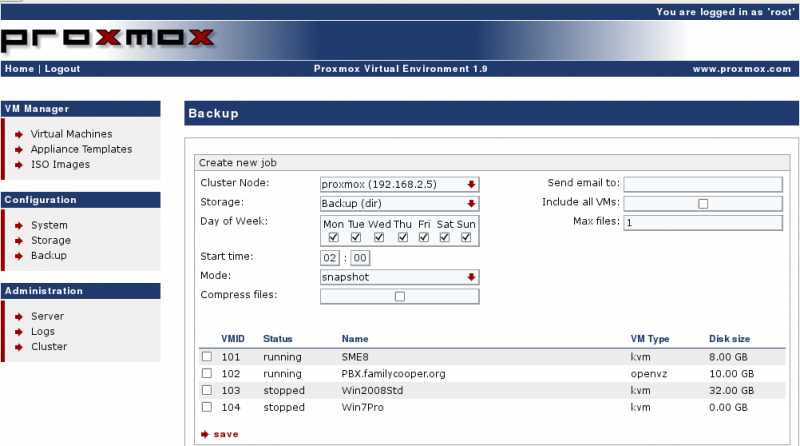
DAHDI
PBX on Proxmox/OpenVZ Notes
- Use 64-bit hardware
- Use 64-bit Proxmox
- Use 64-bit guests
- Install DAHDI on Proxmox Host Node (HN)
- Pass through the DAHDI devices to the PBX guests
- Provides timing to (Asterisk) guest containers (CT)
Install DAHDI on the Proxmox (OpenVZ) Host
apt-get -y update apt-get -y install build-essential make libncurses5-dev libcurl3-dev libiksemel-dev pve-headers-`uname -r` cd /usr/src/ wget http://downloads.digium.com/pub/telephony/dahdi-linux-complete/dahdi-linux-complete-current.tar.gz tar zxfv dahdi-linux-complete-current.tar.gz cd dahdi-linux-complete<tab> make all make install make config
Edit /etc/dahdi/modules and comment out all modules unless you need them:
nano /etc/dahdi/modules modprobe dahdi_dummy
Enable DAHDI Timing in Guest Containers

amportal restart
Storage
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Storage_Model
Supported storage technologies:
- Local storage (mandatory)
- iSCSI
- FC
- NFS
Shared Storage
- In order to use live migration, all virtual disks needs to be stored on SAN, NAS or DRBD storage
- OpenVZ containers must be on local storage or NFS
- OpenVZ live migration works on NFS or local storage
iSCSI
See also napp-it ZFS Storage Server.
LVM Groups with Network Backing
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Storage_Model#LVM_Groups_with_Network_Backing
In this configuration, network block devices (iSCSI targets) are used as the physical volumes for LVM logical volume storage. This is a two step procedure and can be fully configured via the web interface.
- Add the iSCSI target
- On some iSCSI targets you need to add the IQN of the Proxmox VE server to allow access
- Click
Add iSCSI Targeton the Storage list - As storage name use whatever you want but take care, this name cannot be changed later
- Give the 'Portal' IP address or servername and scan for unused targets
- Disable
use LUNs direcly - Click save
- Add LVM group on this target
- Click
Add LVM Groupon the Storage list - As storage name use whatever you want but take care, this name cannot be changed later
- For
Base Storage, use the drop down menu to select the previously defined iSCSI target - For
Base Volumeselect a LUN - For
Volume Group Namegive a unique name (this name cannot be changed later) - Enable shared use (recommended)
- Click
Save
Clustering
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Proxmox_VE_2.0_Cluster
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/High_Availability_Cluster
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Two-Node_High_Availability_Cluster
http://188.165.151.221/threads/9041-Advice-on-Shared-Storage-for-Proxmox-Cluster
http://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Intel_Modular_Server_HA
- Proxmox cluster does not need a dedicated management node
- You can connect to the web interface of any node to manage the entire cluster
- If a virtual machine or container (VM or CT) is configured as HA and the physical host fails, the VM is automatically restarted on one of the remaining Proxmox VE Cluster nodes
User Management
Authentication
Management
Templates
TurnKey OpenVZ Templates
Troubleshooting
Many command line tips here: http://forum.proxmox.com/archive/index.php/t-8624.html
Leftover VM from Failed CT Creation
Try logging into the PVE host and deleting the configuration file of the problem CT:
rm /etc/pve/nodes/pve1/openvz/1000.conf